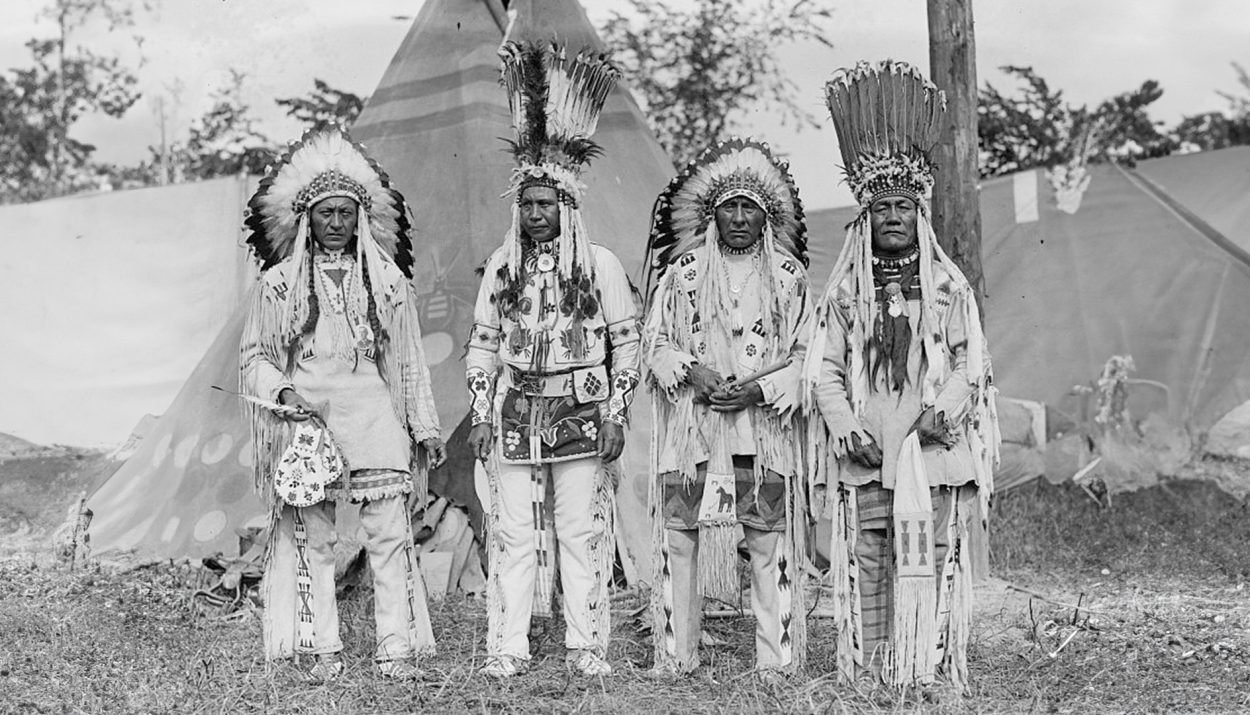
Native American nations have a rich and diverse cultural heritage that spans thousands of years. From the Apache in the Southwest to the Inuit in the Arctic, each tribe has its own unique traditions, languages, and art forms. These vibrant cultural traditions are an integral part of Native American identity and play a crucial role in shaping their communities.
Quiz 1. Which revered animal was essential for the survival of many Native American tribes on the Plains?
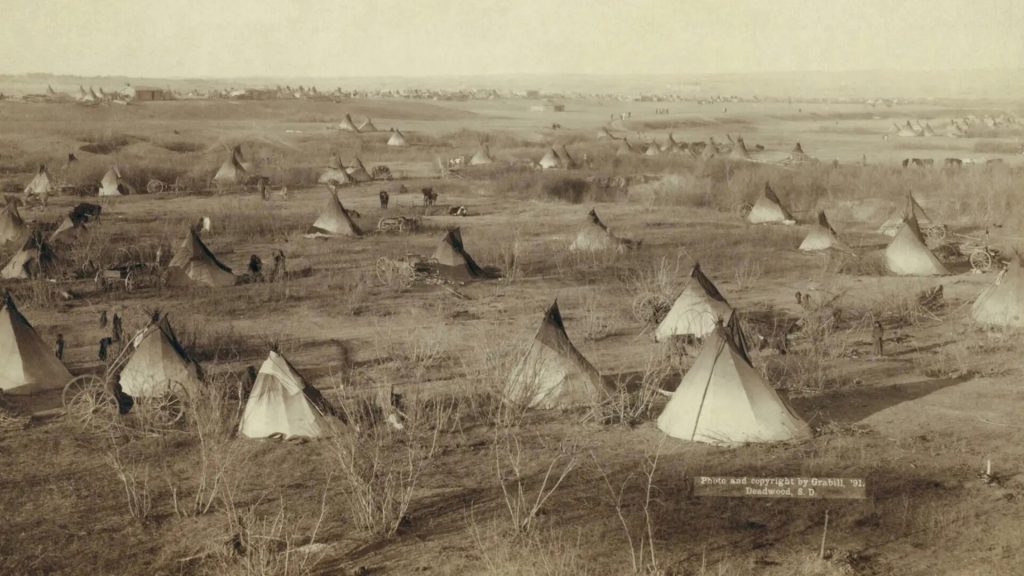

- Elk
- Deer
- Bison
- Salmon
Answer 1. C) Bison

Insight: For Native American tribes on the Plains, the bison wasn’t just an animal – it was essential. From food and clothing to tools and shelter, every part of the bison was used. The sudden decline of the bison in the 1800s devastated these tribes, making them realize how vital bison was to their way of life.
Quiz 2. In which U.S. state is the Chickasaw Nation primarily located?

A. Oklahoma
B. Texas
C. Oregon
D. Nebraska
Answer 2. A) Oklahoma

Insight: The Chickasaw Nation is primarily located in south-central Oklahoma, where their government and cultural institutions are headquartered in Ada. This area is integral to their identity and history, although their ancestral lands were originally in the southeastern United States.
Quiz 3. Upon settling into more permanent settlements, the Ancestral Puebloans started cultivating certain staple crops. Which trio of crops constituted their staple foods?

A. Potatoes, squash, and chilies
B. Corn, squash, and beans
C. Corn, potatoes, and tomatoes
D. Wheat, barley, and rye
Answer 3. B) Corn, squash, and beans

Insight: The Ancestral Puebloans relied on a crucial trio of crops: corn, squash, and beans. Nicknamed the “Three Sisters,” these plants provided a balanced diet and fueled their shift to permanent settlements. Each crop offered vital nutrients and worked together in harmony. Beans climbed the corn stalks and enriched the soil, while squash sprawled beneath the corn, conserving moisture.
Quiz 4. In which region was the Western Apache located?

A. Southeast
B. Southwest
C. Great Basin
D. Plains
Answer 4. B) Southwest

Insight: The Western Apache lived in the diverse landscape of the Southwest region of the United States, where mountains, valleys, and deserts suited their nomadic way of life. Their name “Apache” might come from a Zuni word for “enemy,” reflecting conflicts with neighboring tribes.
Quiz 5. Which Native American tribe’s mysterious disappearance has sparked questions and investigations?

A. Apache
B. Anasazi
C. Lakota
D. Iroquois
Answer 5. B) Anasazi
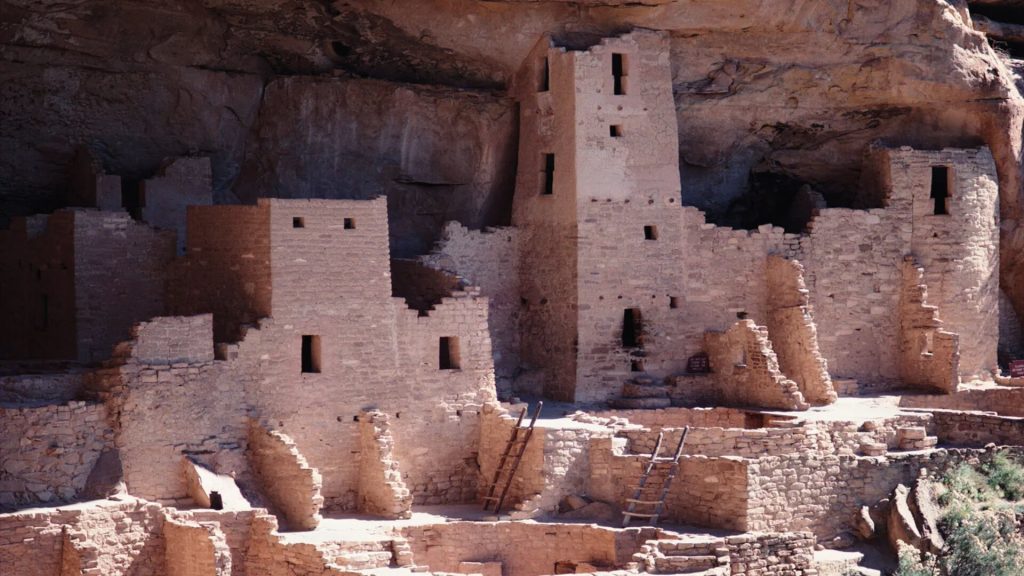

Insight: The Anasazi, an ancient civilization in the Four Corners region, vanished around the 13th century, unlike other tribes who are still around. This mystery has led to theories about their fate, such as climate change or social pressures causing them to move and become the ancestors of modern Pueblo peoples.
Quiz 6. What is the concluding line of the renowned surrender speech by the Nez Perce leader Chief Joseph?

A. “Peace will guide us.”
B. “My heart is heavy.”
C. “I shall return.”
D. “From where the sun now stands I will fight no more forever.”
Answer 6. D) “From where the sun now stands I will fight no more forever.”
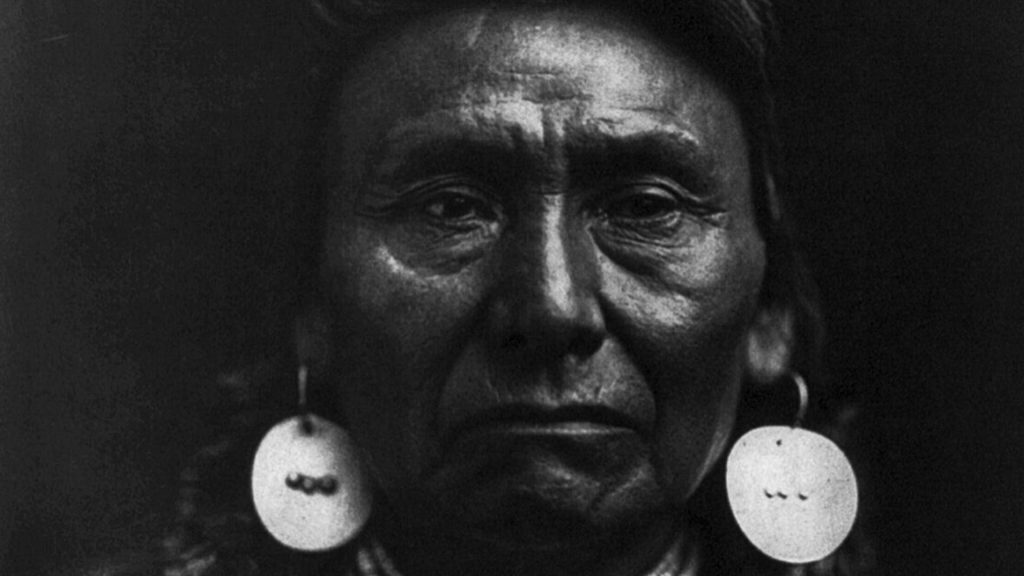

Insight: Chief Joseph’s surrender in 1877, marked by his famous words “From where the sun now stands I will fight no more forever,” was a poignant moment in American history. It signified the end of a long and brutal struggle for the Nez Perce tribe, but more than just surrender, it reflected Chief Joseph’s deep commitment to protecting his people from further suffering. Despite the hardship, his words have endured as a symbol of resilience and the pursuit of peace.
Quiz 7. Geronimo was a prominent figure belonging to which Native American tribe?

A. Cherokee
B. Navajo
C. Mohawk
D. Apache
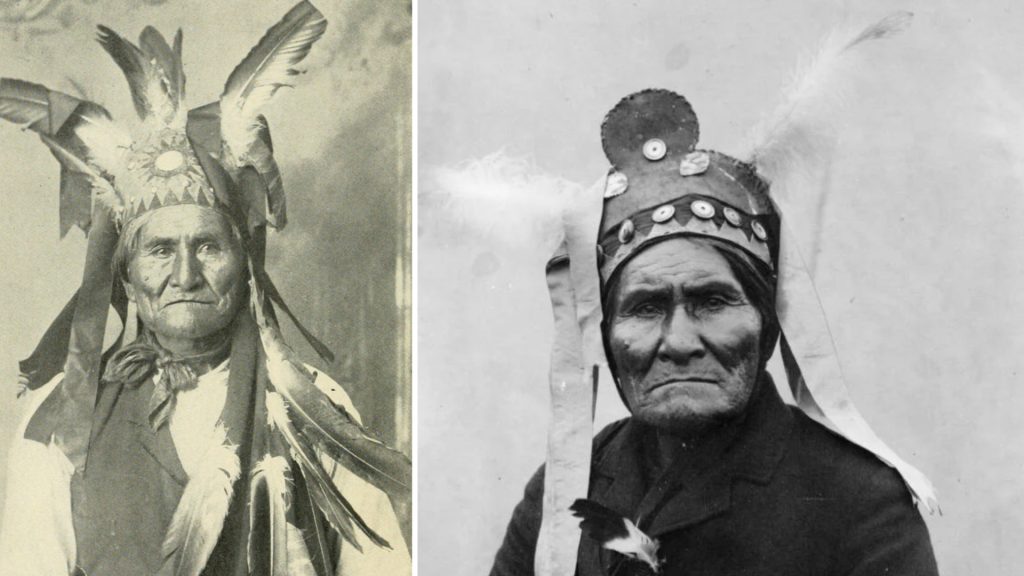
Answer 7. D) Apache

Insight: Geronimo, a Chiricahua Apache leader, fiercely resisted colonization by both Spain and the United States. His strategic skills and unwavering defiance made him a legend in Apache history and a symbol of Native American resistance during a time of great upheaval.
Quiz 8. From which region did the Miami tribe originate?

A. Great Basin
B. Sub-Arctic
C. Eastern Woodland
D. Pacific Northwest
Answer 8. C) Eastern Woodland
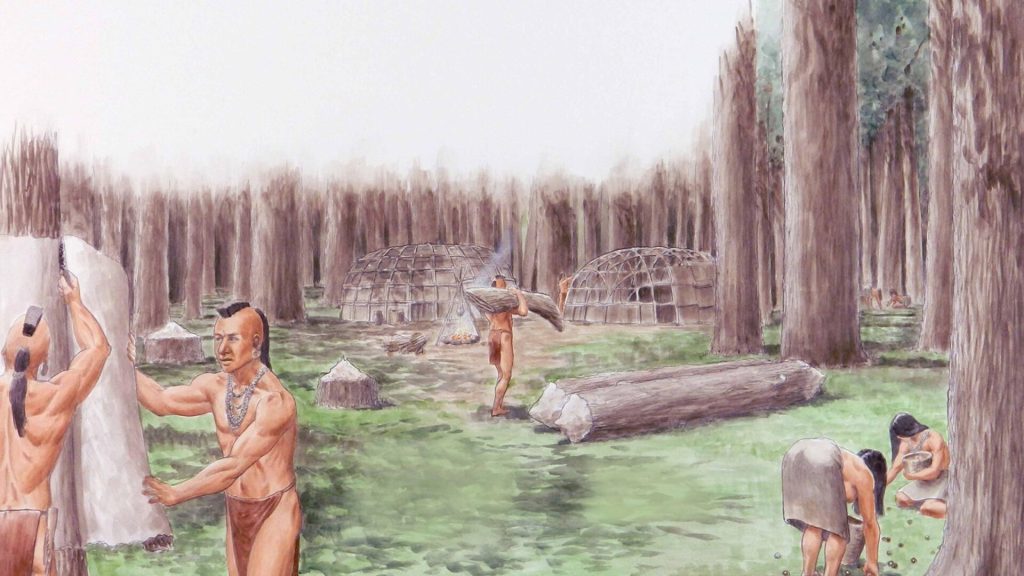

Insight: The Miami tribe, originally from the Great Lakes region, thrived in the Eastern Woodlands environment. Surrounded by forests and rivers, they hunted, gathered, and later fur-traded, developing a culture deeply connected to the land.
Quiz 9. In which region were the Sioux Native American tribes primarily located?

A. Sub-Arctic
B. Southwest
C. Plains
D. Great Basin
Answer 9. C) Plains
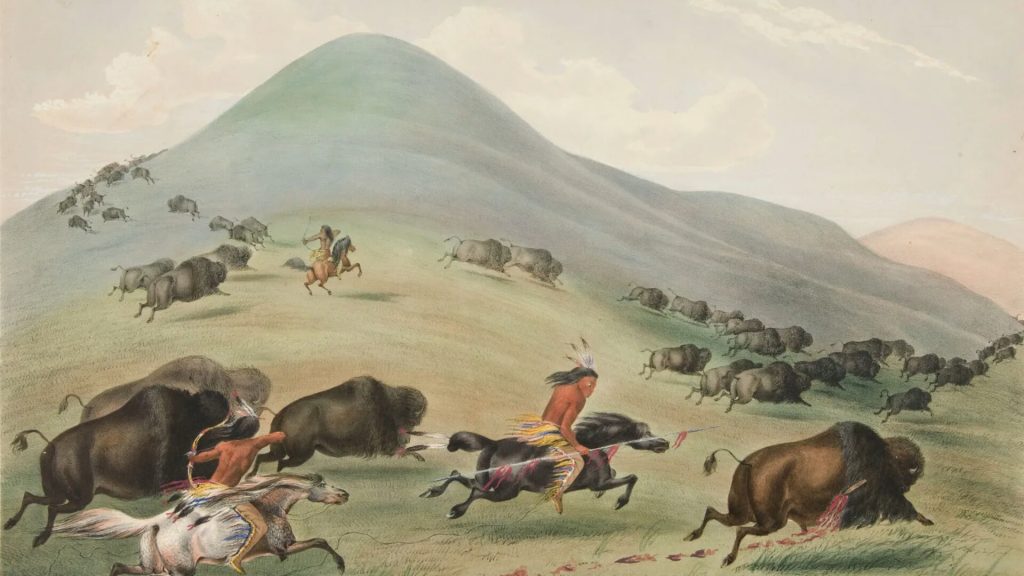

Insight: The Sioux, skilled horsemen and warriors, lived on the Great Plains, a vast region in the central US. They hunted buffalo on these plains, and this animal was central to their way of life. The Great Plains were home not just for hunting, but also for the Sioux culture and history.
Quiz 10. The Labrador Inuit originated from which geographical region?
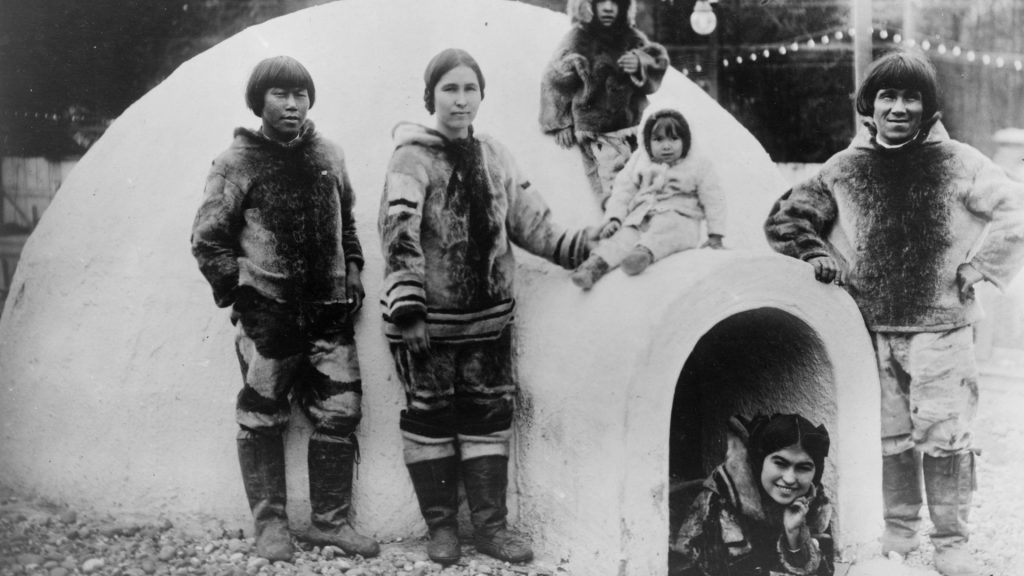

A. Subarctic
B. Southeast
C. Northwest
D. Plateau
Answer 10. A) Subarctic
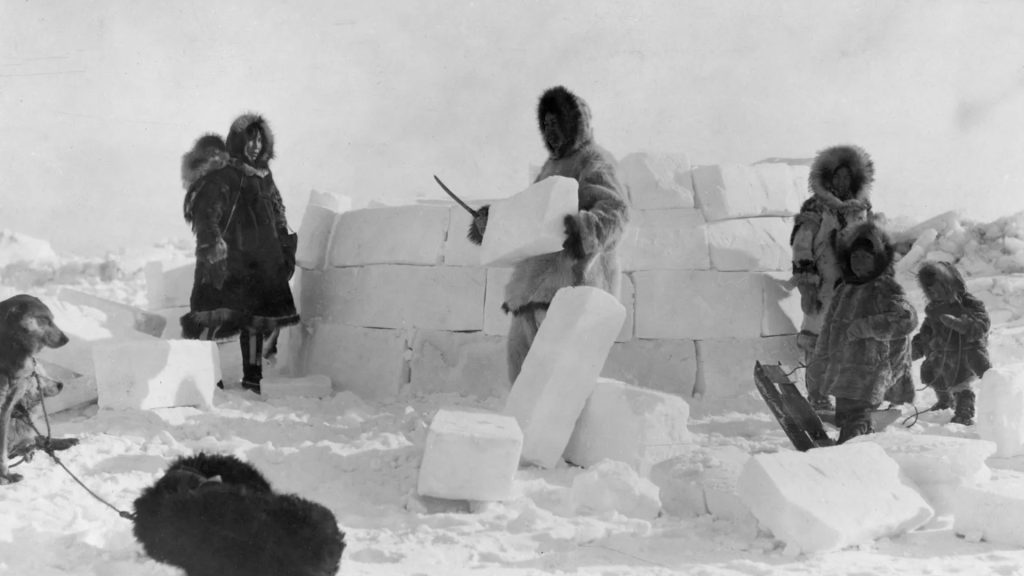

Insight: The Labrador Inuit, living in the cold and icy sub-Arctic regions of Canada and Greenland, were masters of adaptation. They thrived by hunting and fishing in this harsh environment, and even their games, like the ring and pin game, helped them develop the skills they needed to survive.
Quiz 11. Which United States President authorized the Indian Removal Act, ultimately leading to the forced relocation of the Cherokee from their ancestral lands?

A. Andrew Jackson
B. Thomas Jefferson
C. James Madison
D. James Monroe
Answer 11. A) Andrew Jackson
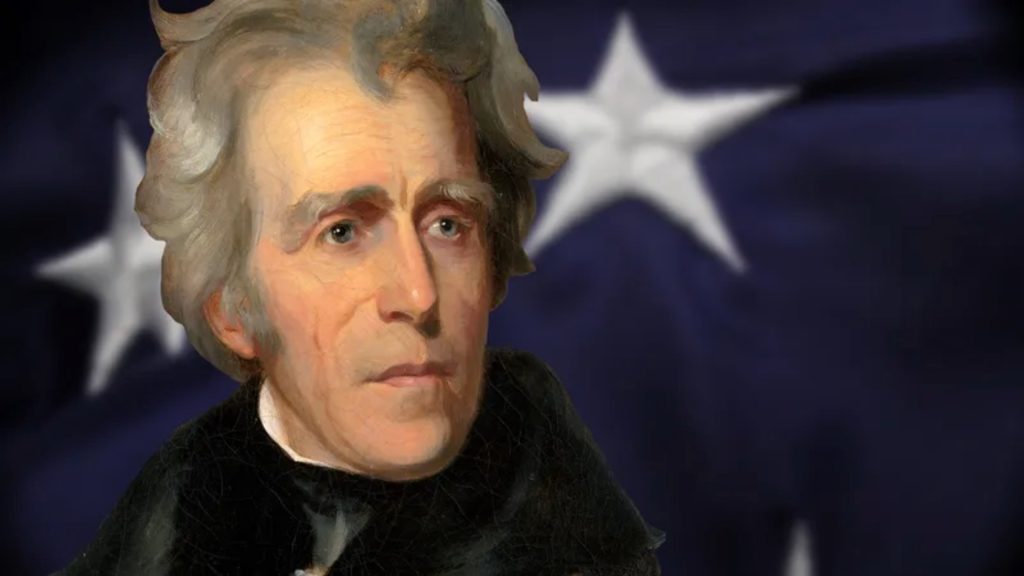

Insight: Andrew Jackson, the 7th president, signed the Indian Removal Act forcing Cherokee and other tribes from their lands. This harsh act is known as the Trail of Tears. Ironically, the Cherokee people had once saved Jackson’s life in battle. This highlights the complex and often contradictory relationship between Jackson and the Native American tribes.
Quiz 12. The Cherokee and the Creek are part of the groups known as the Five Civilized Tribes. Which of these is NOT one of the Five Civilized Tribes?
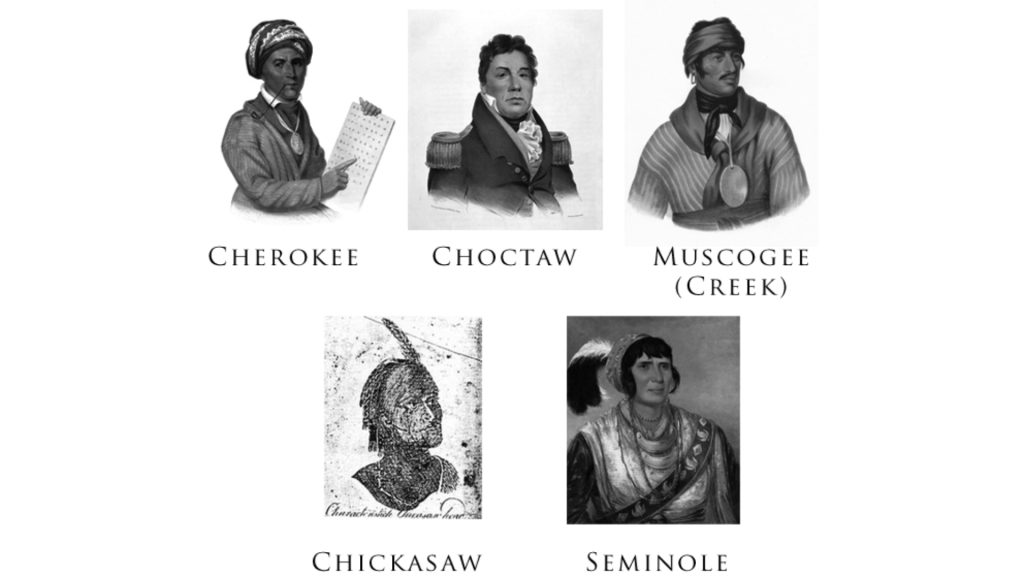

A. Choctaw
B. Comanche
C. Seminole
D. Chickasaw
Answer 12. B) Comanche

Insight: The term “Five Civilized Tribes” refers to Cherokee, Creek, Chickasaw, Choctaw, and Seminole tribes. These Native American groups were seen as adopting European-American ways by the 19th century settlers, unlike the Comanche who remained nomadic on the Great Plains.
Quiz 13. The Chickasaw people share a close relationship with which other tribe?

A. Choctaw
B. Seminole
C. Apache
D. Sioux
Answer 13. A) Choctaw

Insight: The Chickasaw and Choctaw tribes have a long, intertwined history. Once a single people, they eventually became distinct groups but remain culturally close. Today, both are known for their rich heritage and contributions as part of America’s “Five Civilized Tribes.”
Quiz 14. Who is renowned as the most famous Chief of the Nez Perce tribe?

A. Pontiac
B. Chief Joseph
C. Geronimo
D. Black Hawk
Answer 14. B) Chief Joseph

Insight: Chief Joseph, famous for his leadership during the Nez Perce conflict, inherited the role of Chief from his father. He fought for his people’s right to return to their Oregon homeland, but pressure from settlers forced him to surrender. His moving surrender speech, expressing his longing for peace and mourning the loss of his home, cemented his legacy as a symbol of Native American resilience and dignity.
Quiz 15. Which leader was responsible for accepting the surrender of the Nez Perce?

A. Captain Edward Settle Godfrey
B. Major Richard Henry Pratt
C. Colonel Nelson Miles
D. General Gibbon
Answer 15. C) Colonel Nelson Miles

Insight: Colonel Nelson Miles accepted the surrender of Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce tribe in the Bear Paw Mountains on October 5, 1877. This ended a conflict between the Nez Perce and the U.S. government. Chief Joseph’s surrender speech is a famous reminder of this event.
Quiz16. Which reservation holds the title of being the largest in the U.S. by area?

A. Pine Ridge Indian Reservation
B. Navajo Indian Reservation
C. Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation
D. Rosebud Indian Reservation
Answer 16. B) Navajo Indian Reservation
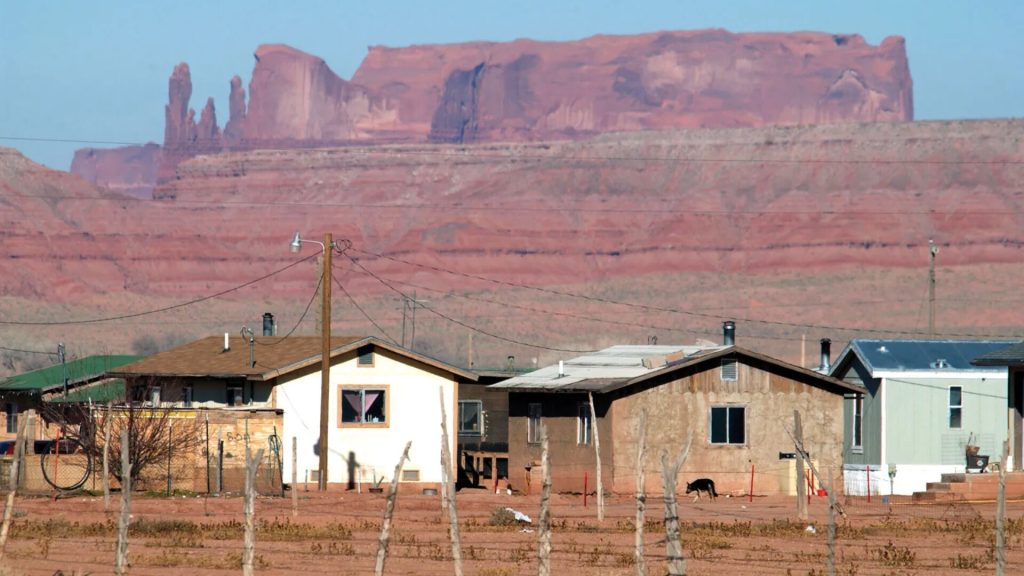

Insight: Spanning a massive 16 million acres across Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah, the Navajo Nation Reservation is the largest in the United States. Established in 1868, it’s more than just a place; it’s a cultural and historical center that embodies the Navajo people’s strength and spirit.
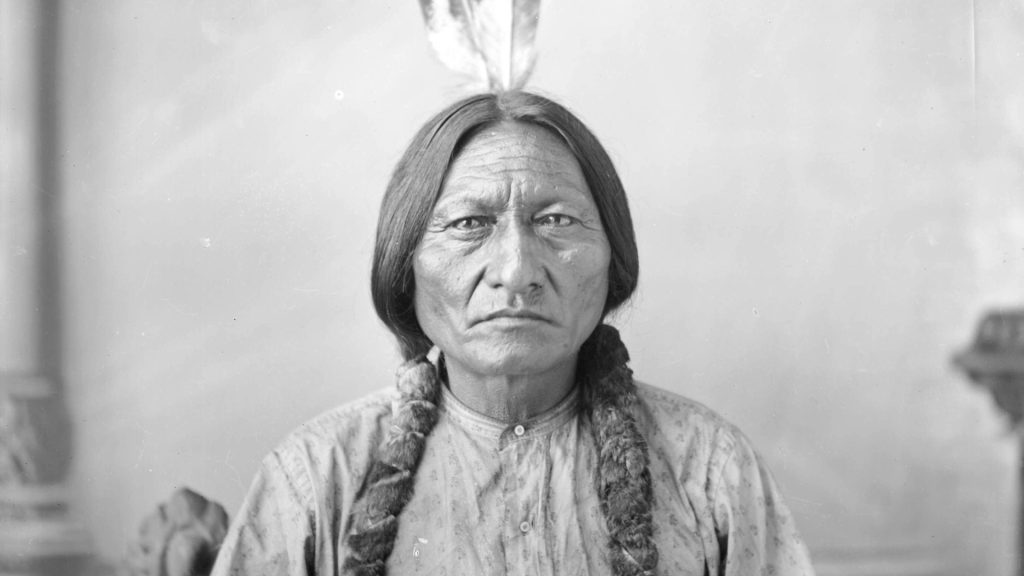
Quiz 17. The renowned Native American leader Sitting Bull belonged to which tribe?

A. Lakota
B. Nez Perce
C. Cherokee
D. Shawnee
Answer 17. A) Lakota

Insight: Sitting Bull, a Lakota leader, played a pivotal role in resisting U.S. expansion onto Native American land. His people, the Lakota, were fierce defenders of their territory. Sitting Bull’s leadership in the Battle of Little Bighorn, a victory over Custer’s forces, stands as a testament to Native American resistance.
Quiz 18. Who invented the Cherokee syllabary without the help of white missionaries and without being literate in English?
A. Stand Watie
B. John Ridge
C. Sequoyah
D. Red Jacket
Answer 18. C) Sequoyah

Insight: Sequoyah, a Cherokee man with no formal education, invented a writing system for his people’s language in 1821. This Cherokee syllabary allowed the Cherokee to finally write their language, helping to preserve their culture and dramatically increase literacy rates. Sequoyah’s creation stands as a powerful example of how one person’s ingenuity can empower a culture.
Quiz 19. What cause of death did the doctor declare on Chief Joseph’s death certificate when he passed away in 1904 at the Colville Reservation?

A. Malaria
B. Old Age
C. Influenza
D. A broken heart
Answer 19. D) A broken heart

Insight: Chief Joseph, a Nez Perce leader, died in 1904 at the age of 64. Though the official cause of death was listed as illness, it is believed heartbreak took a toll on his health. He spent years fighting for his people’s right to return to their homeland but was never allowed to go back.
Quiz 20. Who was responsible for originating the term “Indian”?

A. Amerigo Vespucci
B. Hernán Cortés
C. Christopher Columbus
D. Bureau of Indian Affairs
Answer 20. C) Christopher Columbus

Insight: Christopher Columbus, searching for a westward passage to Asia, landed in the Americas in 1492. Mistakenly thinking he’d reached India, he called the native people “Indians” – a term that stuck but is now considered outdated. Today, “American Indian” or “Native American” are preferred, recognizing the variety of cultures that thrived in the Americas before European arrival.
Quiz 21. From which area does the Muckleshoot tribe originate?

A. Washington
B. New Mexico
C. Arizona
D. California
Answer 21. A) Washington

Insight: The Muckleshoot Tribe, from Washington State’s Puget Sound area, has a rich cultural tradition. Their ancestors thrived for generations along the eastern shores and cascading rivers, forging a deep connection to the land that continues to define the Muckleshoot identity today.
Quiz 22. During the mid-1800s, the Trail of Tears tragically involved the forced relocation of several Native American tribes. Which tribe was NOT part of this forcible removal?

A. Apache
B. Seminole
C. Chickasaw
D. Cherokee
Answer 22. A) Apache

Insight: The Trail of Tears forced the Cherokee, Choctaw, Creek, Seminole, and Chickasaw tribes from their southeastern homes to Oklahoma. This event didn’t impact the Apache, who lived in the Southwest. They faced their own struggles with the U.S. government later on, with figures like Geronimo leading resistance.
Quiz 23. What is the English translation of ‘Nez Perce’?

A. Silent Forest
B. Thundering Water
C. Pierced Nose
D. Mountain
Answer 23. C) Pierced Nose
Insight: The Nez Percé people are called “Pierced Nose” by French fur traders, a misnomer since the tribe didn’t pierce noses. This highlights how outsiders can influence the names and identities of indigenous groups, even if inaccurate.
Quiz 24. What method did the great houses of Chaco Canyon use to communicate with their peripheral settlements?

A. Messenger birds
B. Drum messaging
C. Signal fires
D. Semaphore flags
Answer 24. C) Signal fires

Insight: The great houses of Chaco Canyon used a clever communication system with signal fires positioned on high points. These fires, possibly amplified by reflective rock, were visible for long distances across a network of stations. This allowed the Ancestral Puebloans to relay messages and stay connected.
Quiz 25. With which tribe is Chief Running Coyote associated?

A. Cherokee
B. Seminole
C. Crow
D. Sioux
Answer 25. C) Crow

Insight: The Crow tribe, also known as the Apsaalooke, were known for their cleverness and skill on the Great Plains. One of their most famous leaders, Chief Running Coyote, is credited with inventing the buffalo jump, a hunting method that used cliffs to stampede bison for a large supply of meat and materials. This technique exemplifies the Apsaalooke’s ingenuity and resourcefulness in their environment.
Quiz 26. The Cherokee Native Americans originally hailed from which region of the country?

A. Northwest
B. Northeast
C. Southeast
D. Great Plains
Answer 26. C) Southeast

Insight: The Cherokee, one of the largest and most organized tribes in the Southeast, lived in what is now North Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia, and Alabama. They farmed, hunted, and traded, and called themselves the “Principal People.” Sadly, their history was marked by the forced relocation known as the Trail of Tears.
Quiz 27. Who were the main military leaders pursuing the Nez Perce tribe in 1877?

A. Gen. Robert E. Lee and Col. Theodore Roosevelt
B. Gen. Oliver Howard and Col. Nelson Miles
C. Gen. McClelland and Col. Klink
D. Gen. Sherman and Col. Mustard
Answer 27. B) Gen. Oliver Howard and Col. Nelson Miles

Insight: In 1877, the Nez Perce tribe, led by Chief Joseph, tried to escape to Canada to avoid reservation life. General Howard and Colonel Miles relentlessly pursued them for months, showcasing the struggles between Native Americans and the U.S. government during westward expansion.
Quiz 28. Among the hunting tools utilized by the Anasazi, one was a specific type of dart or spear thrower. What is its name?

A. Atlatl
B. War Club
C. Bowstaff
D. Kiva
Answer 28. A) Atlatl

Insight: The atlatl was a hunting tool used by ancient cultures like the Anasazi. It functioned as an extension of the arm, throwing darts or spears farther and with more force than by hand. Made of wood and sometimes featuring a leather grip, it had a hook or notch to hold the projectile. This design shows the ingenuity of early people in improving their hunting abilities.
Quiz 29. The Arapaho tribes were traditionally inhabitants of which kind of area?

A. Plains
B. Rainforests
C. Mountains
D. Swamps
Answer 29. A) Plains

Insight: The Great Plains, a vast expanse of grasslands stretching from the Mississippi River to the Rockies, was home to the Arapaho tribes. This environment perfectly suited their way of life. The abundant buffalo and other game on the plains provided the Arapaho with not just sustenance, but also the materials needed for their culture.
Quiz 30. During the Trail of Tears, what was the leading cause of death among those who perished?

A. Infectious diseases
B. Heart Attack
C. Exhaustion
D. Animal attacks
Answer 30. A) Infectious diseases

Insight: Infectious diseases were the main cause of death on the Trail of Tears. Harsh conditions and a weakened immune system made the Cherokee people more susceptible to illnesses like cholera and smallpox. These diseases, brought by Europeans centuries ago, devastated the Indigenous populations.
Quiz 31. How many tribal governments have federal recognition in the United States?

A. 428
B. 574
C. 269
D. 6,204
Answer 31. B) 574

Insight: You are right, there are 574 federally recognized tribal governments in the United States. This special status allows them to govern themselves and have a legal relationship with the U.S. federal government.
Quiz 32. Which tribe is renowned for creating Kachina dolls?
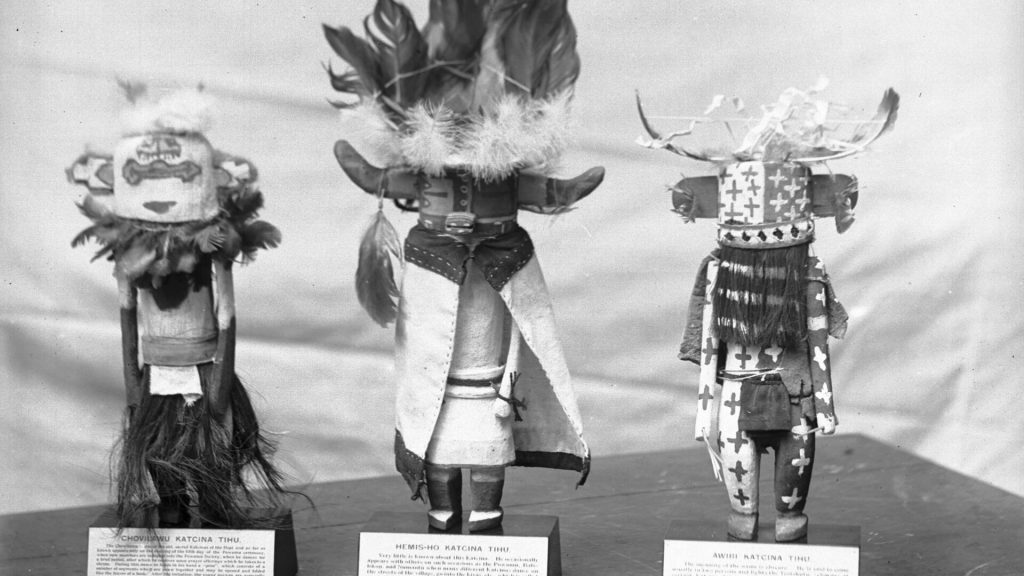

A. Navajo
B. Seminole
C. Pueblo
D. Hopi
Answer 32. D) Hopi

Insight: The Hopi people carve Kachina dolls to teach their children about their religion and culture. Each doll represents a Kachina spirit, which is important in Hopi ceremonies. This tradition shows how much the Hopi value their beliefs and passing them on to younger generations.
Quiz 33. In 1861, the Navajo experienced a tragic event similar to the Cherokee “Trail of Tears,” where individuals were marched into captivity at Fort Sumner, resulting in many deaths. What is the name of this sorrowful journey?

A. The Journey of Desolation
B. The Long Walk
C. The Great March
D. The Path of Tears
Answer 33. B) The Long Walk

Insight: The Long Walk of the Navajo, similar to the Cherokee Trail of Tears, was a forced relocation of thousands of Navajo people from their homeland in 1864. They were marched hundreds of miles to Fort Sumner in harsh conditions, with many suffering and dying along the way. This event serves as a reminder of the hardships faced by Native Americans during forced assimilation by the U.S. government.
Quiz 34. Religion was a significant aspect of Anasazi culture. What name was given to their religious buildings?

A. Totemas
B. Kachinas
C. Kivas
D. Pueblos
Answer 34. C) Kivas
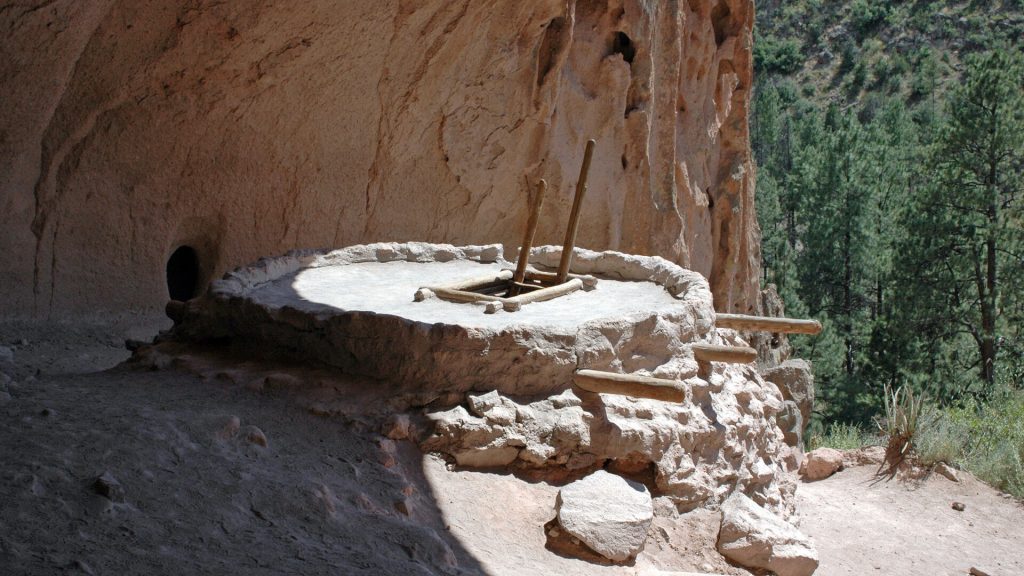

Insight: Kivas were central to the Anasazi way of life. These underground ceremonial structures hosted religious rituals and community gatherings. Their design, with a rooftop entrance and a sipapu (a hole symbolizing an ancestral portal), reflects how deeply intertwined Anasazi architecture and spirituality were.
Quiz 35. Approximately how many members does the Choctaw tribe currently have?

A. 120,000
B. 225,000
C. 800,000
D. 5,000,000
Answer 35. B) 225,000

Insight: The Choctaw Nation is one of the largest Native American tribes in the United States, with a membership of roughly 225,000 individuals. This makes it the third-largest Indigenous Nation in the U.S. The tribe has a rich history and culture that has been preserved and passed down through generations.
Quiz 36. After the Pilgrims landed at Plymouth Rock, which tribe extended their friendship towards them?

A. Cherokee
B. Iroquois
C. Passamaquoddy
D. Wampanoag
Answer 36. D) Wampanoag

Insight: The Wampanoag tribe, led by Massasoit, befriended the Pilgrims upon their arrival at Plymouth Rock. They not only offered the newcomers a warm welcome but also shared crucial knowledge for survival. The Wampanoag taught the Pilgrims how to grow essential crops like beans and squash, which helped the settlers adapt to their new environment. This initial cooperation between the two groups laid the foundation for a peaceful period, eventually leading to the very first Thanksgiving celebration.
Quiz 37. From which region did the Potawatomi originate?

A. Midwest
B. Sub-Arctic
C. Southeast
D. Pacific Northwest
Answer 37. A) Midwest
Insight: The Potawatomi people originally lived in Michigan’s lower peninsula, but pressure from European settlers forced them to move westward. They adapted to new environments, eventually settling in Wisconsin, Indiana, and Illinois. This highlights their resilience in the face of change.
Quiz 38. Which other tribe is most closely related to the Navajos?

A. Sioux
B. Iroquois
C. Aztec
D. Apache
Answer 38. D) Apache

Insight: The Navajo and Apache tribes share a deep bond due to their common Athabascan language and heritage. Having migrated to the Southwest together around 1400 AD, their linguistic and genetic ties highlight their close relationship as relative newcomers to the region.
Quiz 39. Which tribe proudly carries the title of ‘Unconquered People’?

A. Seminole
B. Sioux
C. Cherokee
D. Navajo
Answer 39. A) Seminole

Insight: The Seminole people earned their nickname, “The Unconquered People,” through their resistance against the U.S. military in the 1800s. Despite efforts to remove them, some Seminoles remained in Florida, preserving their culture. Today, their descendants live on, honoring their ancestors’ strength and resilience.
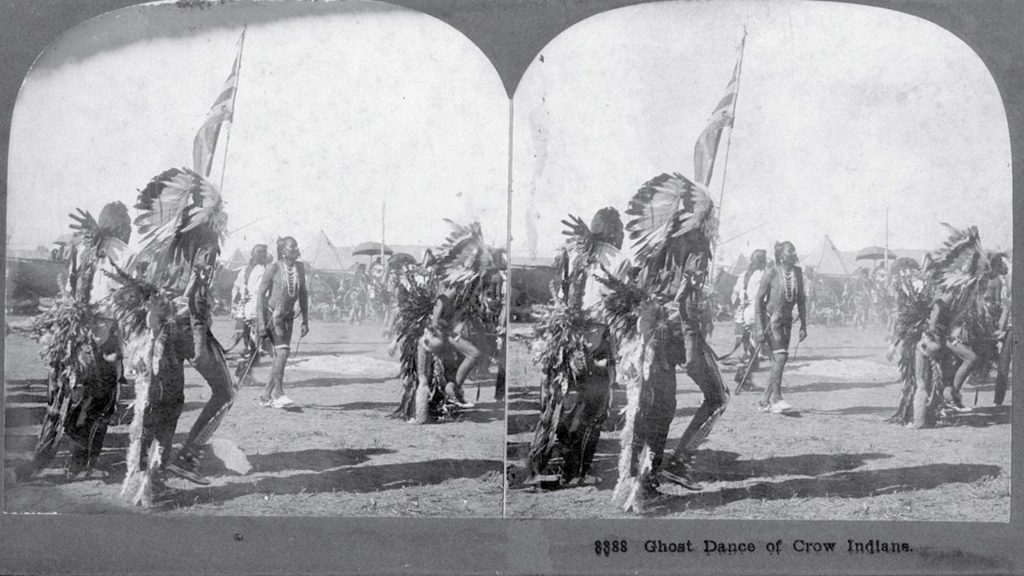
Quiz 40. In the 1890s, a spiritual leader from which tribe sparked the Ghost Dance movement?

A. Osage
B. Paiute
C. Apache
D. Skokomish
Answer 40. B) Paiute

Insight: The Ghost Dance movement, sparked by a vision of hope and renewal from a Northern Paiute shaman named Wovoka, united various Plains tribes in 1889. This spiritual movement stands as a testament to both the enduring strength of Native American cultures and their yearning for a better future.
Quiz 41. Who was the first European explorer to encounter the Cherokee?

A. Columbus
B. Cabot
C. Cortes
D. De Soto
Answer 41. D) De Soto

Insight: In 1540, Hernando de Soto became the first European to encounter the Cherokee people in the southeastern United States, marking a turning point for both the Cherokee and European exploration in North America. His expedition also led him to the Mississippi River, further solidifying European presence on the continent.
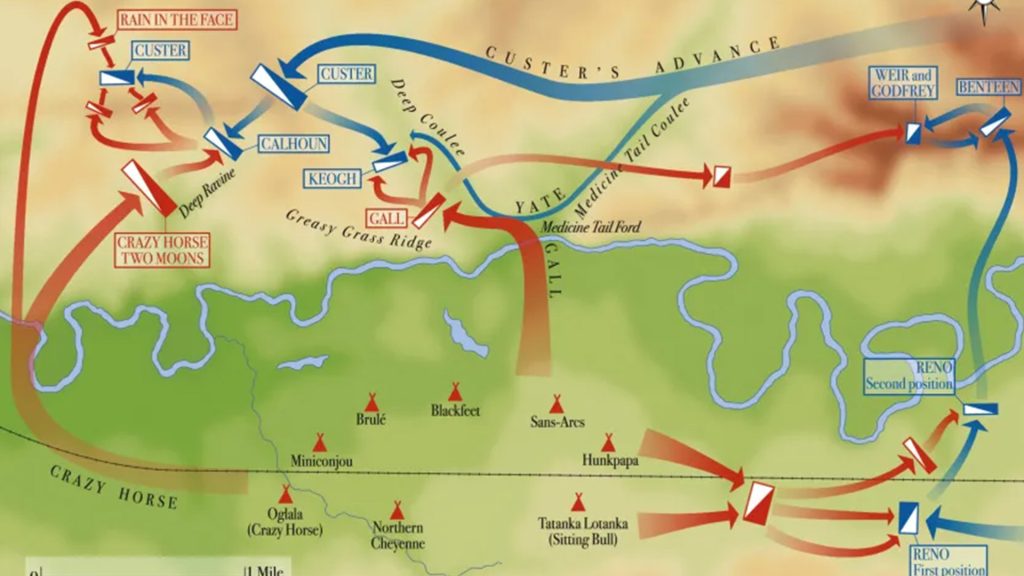
Quiz 42. Which tribe emerged victorious against George Custer’s battalion during the Battle of the Little Bighorn?
A. Apache
B. Lakota
C. Cherokee
D. Sioux
Answer 42. B) Lakota

Insight: The Battle of the Little Bighorn, also known as Custer’s Last Stand, was a fight between the Lakota Sioux and Cheyenne tribes, and the U.S. Army led by Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer. It took place on June 25 and 26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River. The Lakota and Cheyenne were victorious, marking a significant win for Native American tribes against the U.S. Army.
Quiz 43. Who is the author of the book Bury My Heart At Wounded Knee?

A. Dee Brown
B. James Fenimore Cooper
C. Helen Hunt Jackson
D. Sherman Alexie
Answer 43. A) Dee Brown

Insight: Dee Brown’s “Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee” chronicles the brutal reality of Native American experiences in the 1800s. Using in-depth research and a powerful narrative, the book exposes the injustices they endured as the US government forced them from their lands. This critical look at westward expansion highlights the suffering of Indigenous peoples, making it a vital read for anyone seeking the truth about this period in American history.
Quiz 44. Which Native American tribe is recognized as the largest in the United States by population?
A. Cherokee
B. Osage
C. Modoc
D. Navajo
Answer 44. A) Cherokee

Insight: With over 450,000 tribal citizens, the Cherokee Nation is the largest tribe in the United States. They have a rich cultural heritage and a significant presence in northeastern Oklahoma, where more than 141,000 citizens reside. Though not the biggest in land area, the Cherokee Nation’s size and history make it a key player in discussions about Native American affairs.
Quiz 45. The Navajo Reservation, sprawling across the Four Corners region, is comparable in size to which U.S. state?
A. West Virginia
B. Alaska
C. Utah
D. Texas
Answer 45. A) West Virginia

Insight: The Navajo Reservation is massive, stretching over 27,000 square miles, comparable to the size of West Virginia. Encompassing parts of Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah, this vast territory showcases a diversity of landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to alpine forests.
Quiz 46. In the native language, what does ‘Kiowa’ translate to?

A. River Folk
B. Principal People
C. Dust Storm
D. Warrior Clan
Answer 46. B) Principal People

Insight: The Kiowa tribe called themselves “Principal People” in their own language, reflecting their pride in their central role and importance among the tribes of the Great Plains. They were a pivotal group, forming alliances and interacting with others like the Crow. Their name signifies both their leadership and their unique identity.
Quiz 47. From which tribe does the Indian writer N. Scott Momaday hail?

A. Hopi
B. Mohawk
C. Kiowa
D. Blackfoot
Answer 47. C) Kiowa

Insight: N. Scott Momaday, a Kiowa author, drew inspiration from his Native American heritage to write novels and poems that shed light on Native American experiences. His work, including the Pulitzer Prize-winning novel “House Made of Dawn,” was instrumental in bringing these stories to a wider audience.
Quiz 48. During World War I, which Native American tribe’s members famously served as ‘code talkers,’ utilizing their native language to transmit encoded messages?
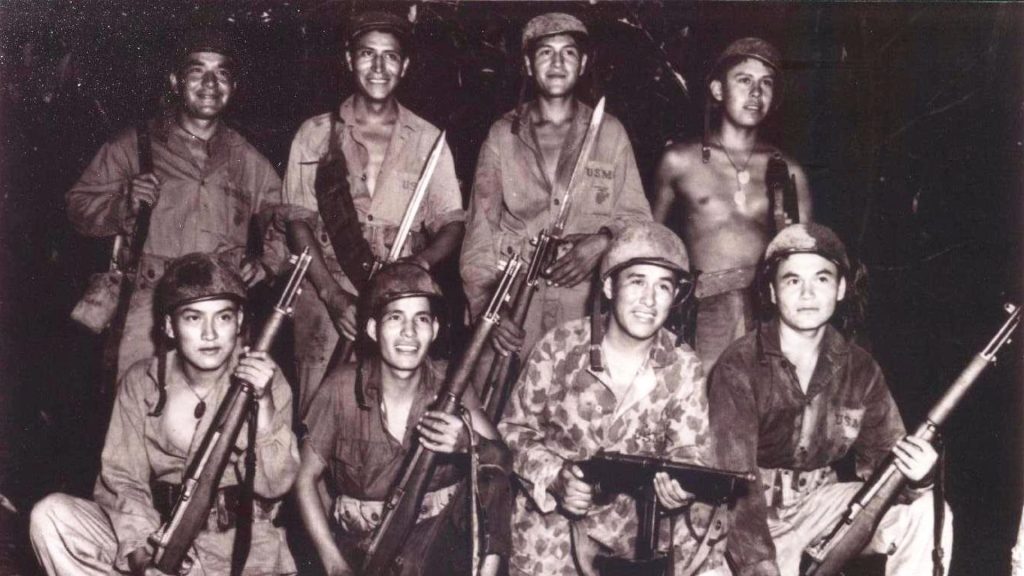

A. Seminole
B. Snoqualmie
C. Choctaw
D. Apache
Answer 48. C) Choctaw

Insight: The Choctaw Nation played a key role in World War I by using their language as a code to transmit messages. This unique code, impossible for the Germans to crack, helped ensure the secrecy of military operations and ultimately contributed to Allied victory. Their success inspired other Native American tribes to follow suit in future wars.
Quiz 49. What is the current name for the group historically known as the Diné Indians?

A. Kiowa
B. Cherokee
C. Navajo
D. Blackfoot
Answer 49. C) Navajo

Insight: The Diné people, later known as Navajo, are a large Native American tribe with a rich history. Their preferred term is “Diné,” which means “The People,” but “Navajo” is more widely used today. This reflects the Navajo’s adaptation to the modern world while still maintaining their cultural identity.
Quiz 50. Which tribe formed an alliance with the French to oppose the Illiniwek during the early 18th century?

A. Peoria
B. Navajo
C. Blackfoot
D. Osage
Answer 50. D) Osage

Insight: The Osage Nation allied with the French in the 1700s to fight rival tribes. This alliance showed their skills in war and trade. By getting guns and horses from the French, the Osage became even stronger militarily and economically. This was an important time in Osage history as they adapted to the changing situation in North America.
Quiz 51. Who is the Native American author behind the book Love Medicine?

A. Teresa James
B. Louise Erdrich
C. N. Scott Momaday
D. Sherman Alexie
Answer 51. B) Louise Erdrich

Insight: Louise Erdrich, a Chippewa and Ojibwe author, explores the complexities of Native American life through her novel “Love Medicine”. This debut novel, which won the National Critics Circle Book Award, covers themes of history, culture, and family relationships. Erdrich’s writing provides a window into the struggles and triumphs of Native Americans, making her a prominent voice in Native American literature.
Quiz 52. Which U.S. general was in command during the forced relocation of the Cherokee people, known as the Trail of Tears?

A. William Tecumseh Sherman
B. Winfield Scott
C. George Armstrong Custer
D. Andrew Jackson
Answer 52. B) Winfield Scott

Insight: The Trail of Tears was the forced relocation of the Cherokee people by the U.S. government in the 1830s. Led by General Winfield Scott, thousands of Cherokee were forced to walk hundreds of miles westward, facing starvation, disease, and death. This event is a dark stain on American history.
Quiz 53. The Ponca tribe originally inhabited which region of the United States?
A. Northeast
B. Pacific Northwest
C. Midwest
D. Rocky Mountains
Answer 53. C) Midwest

Insight: The Ponca tribe, a group with a rich history, originally lived around the Ohio River Valley. Over time, they adapted and migrated westward to what are now Nebraska, Iowa, and South Dakota. This movement shows their resilience and ability to thrive in different environments across the Midwest.
Quiz 54. Approximately how many miles were the Cherokees compelled to march during their forced removal?

A. 800 miles
B. 50 miles
C. 2,200 miles
D. 1,100 miles
Answer 54. C) 2,200 miles

Insight: The Trail of Tears was a forced relocation of the Cherokee people from their ancestral lands in the southeastern United States to present-day Oklahoma in the late 1830s. This harrowing journey of approximately 2,200 miles resulted in immense suffering and loss for the Cherokee, with thousands dying from disease, exposure, and starvation.
Quiz 55. Many Navajos reside close to a revered landform known as?

A. Antelope Canyon
B. Monument Valley
C. Devil’s Tower
D. Canyon de Chelly
Answer 55. D) Canyon de Chelly

Insight: Canyon de Chelly in Arizona is a stunning natural wonder that also holds deep cultural significance for the Navajo people. For centuries, they have lived and farmed within the canyon walls, raising crops and tending to livestock. The canyon has served as both a refuge and a battleground throughout Navajo history. Today, visitors can explore this land and learn about the Navajo people’s enduring culture.
Quiz 56. Which philosopher originated the ‘Noble Savage’ idea?

A. Thoreau
B. Emerson
C. Rousseau
D. Locke
Answer 56. C) Rousseau

Insight: Jean-Jacques Rousseau, an Enlightenment philosopher, believed people in nature were inherently good and untainted by civilization’s corruption. He saw them, like indigenous cultures, as peaceful and morally superior. This idea, though meant to show human purity, led to romanticized stereotypes of these cultures.
Quiz 57. Which tribe was NOT a member of the Iron Confederacy during the 18th century?

A. Crow
B. Cree
C. Stoney
D. Assiniboine
Answer 57. A) Crow

Insight: The Iron Confederacy, a powerful alliance of Native American tribes including the Assiniboine and Cree, played a key role in the fur trade, particularly with the Hudson Bay Company. Unlike the horse-focused Crow tribe, the Iron Confederacy demonstrates the varied political and economic partnerships among Native American groups before European colonization.
Quiz 58. Francis Parkman penned a narrative involving a fierce Native American leader. Which chief was the subject of his writings?

A. Pontiac
B. Tecumseh
C. Crazy Horse
D. Chief Seattle
Answer 58. A) Pontiac

Insight: Francis Parkman’s book “The Conspiracy of Pontiac” explores the aftermath of the French and Indian War on eastern Native American tribes. The book centers around Pontiac, a key leader in the resistance against British expansion. Parkman’s account offers valuable historical insight, but it’s important to remember that his views are influenced by the attitudes of his time period.
Quiz 59. Which tribe is known as the ‘People of the South Wind’?

A. Hopi
B. Kaw
C. Lakota
D. Seminole
Answer 59. B) Kaw

Insight: The Kaw Nation, also known as the “People of the South Wind,” is a Native American tribe with a rich history in the central Midwestern United States. Their deep connection to the land is reflected in their nickname and even the name of the state, Kansas, which honors their legacy.
Quiz 60. The term ‘Anasazi,’ used by the Navajo to describe the Ancestral Puebloans, is not a self-designation. What is its rough translation in English?

A. Ancient builders
B. Ancient enemy
C. Long-time friend
D. Forgotten people
Answer 60. B) Ancient enemy

Insight: “Anasazi,” though once common, is no longer the preferred term for this ancient culture. It translates to “ancient enemy” and is considered disrespectful. Today, we refer to them as “Ancestral Pueblo” or “Ancestral Puebloan” to show respect for their heritage.






