Anybody who grew up in the Cold War Era knows that the threat of nuclear war was real and present. Schools held nuclear drills. Movies depicted what could lead to war and what the world would be like after a nuclear attack. It was scary and we breathed a collective sigh of relief when the Iron Curtain came down. So why does the nuclear threat feel new again?
90 Seconds To Midnight
The Doomsday Clock is a clock that measures how close the world is to catastrophe. It’s specifically tied to technology and the risk that humanity might bring about its own extinction through carelessness and hubris. Given our haste to use technology without fully understanding the ramifications, it’s not a needless worry.

The threat of nuclear war is looming large over the world. Doomsday is midnight on the clock. In early 2024, the Doomsday Clock is 90 seconds away from midnight. It has remained unchanged since 2023, but it’s still the closest to midnight it has ever been.
The History Of The Doomsday Clock
The Doomsday Clock has been a tool used by the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists in Chicago, which updates the time every year. Their decision of where to set the clock is based on the organization’s assessment of catastrophic risks to the human race.
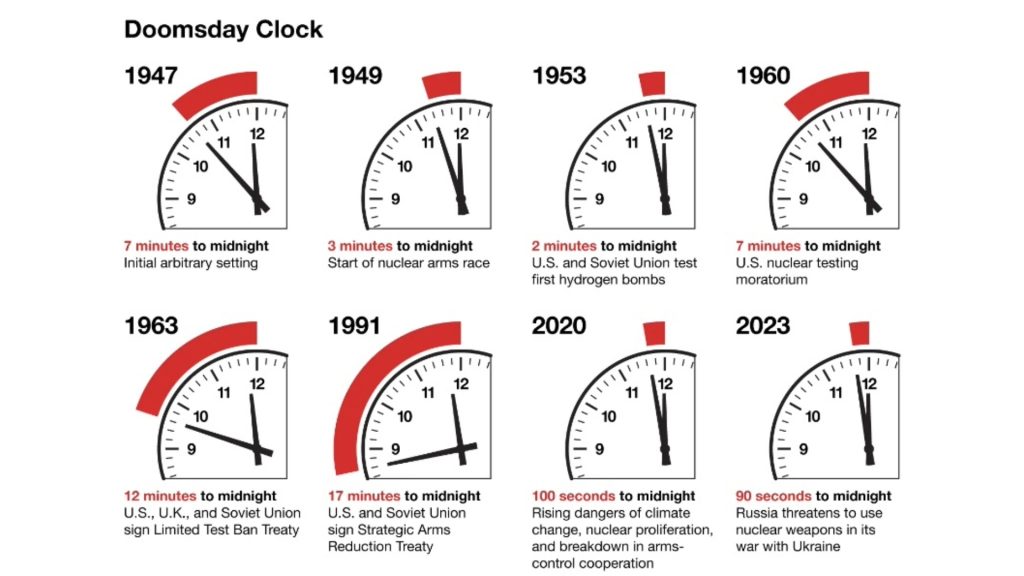
The proximity to midnight has many saying that we’ve never been closer to a World War III that could end life as we know it. A review of the timeline reveals that we’ve lost ground since 1991, when the US and USSR signed the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty.
The Risk of Nuclear Proliferation
Even though the United States has reduced its arsenal of nuclear warheads, there’s still a risk that one launch could lead to an all-out nuclear war. The more nuclear bombs there are in the world, the greater the risk that someone could use one to take us down the path to extinction.

There are plenty of reasons why nuclear scientists have cause to be alarmed by the nuclear situation around the world. There are multiple countries with 100 or more warheads and one whose nuclear capabilities are unknown to us at present.
When Did The Nuclear Arms Race Begin?
The nuclear arms race began in earnest when the United States used two nuclear warheads against civilian populations in Japan. The cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were hit and mostly destroyed. The US remains the only country to have used nuclear weapons in war.

After World War II ended, there was an ongoing effort by other countries to build nuclear bombs. The USSR was the first to do so. They detonated a bomb in 1949 and that kicked off the arms race known as the Cold War. The word “cold” indicated a war that wasn’t active but only implied.
How Long Did The Cold War Last?
If the Cold War started in 1949, when did it end? Most historians would say that the fall of the so-called Iron Curtain was the beginning of the end. The Soviet Union dissolved in 1989, when George H.W. Bush was President of the US.
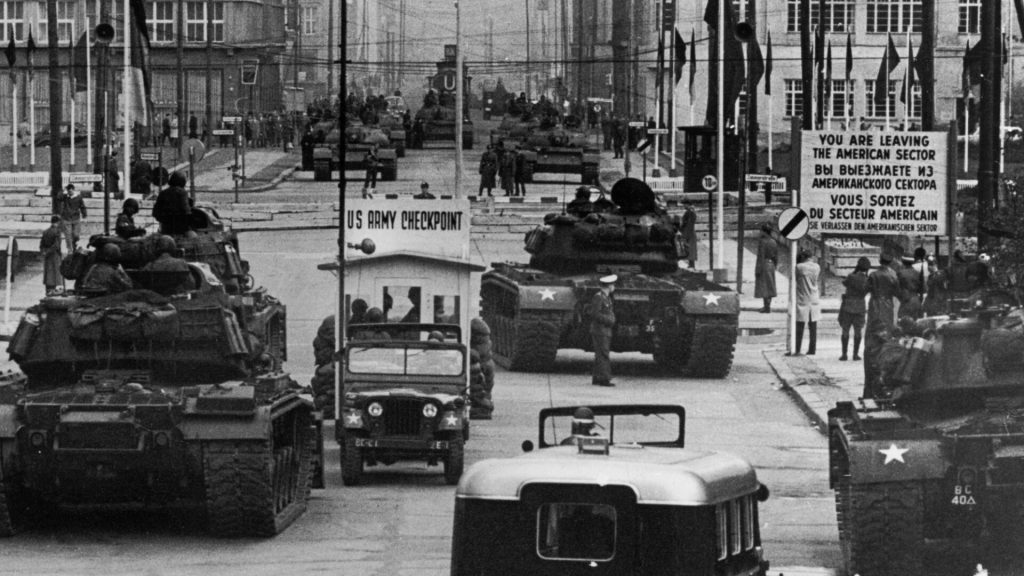

Many credited Bush’s predecessor, Ronald Reagan, with bringing about the fall of the USSR. Certainly Mikhael Gorbachev’s policy of Glasnost, openness in Russian, played a role. But the Cold War needed a couple more years before it truly came to an end.
Mutually Assured Destruction
During the Cold War, the practice was for the world’s largest countries (China, the US, and the USSR) to proliferate nuclear weapons as quickly as they could. The idea was that if each country had enough weapons, no other country would dare to launch a weapon at them.
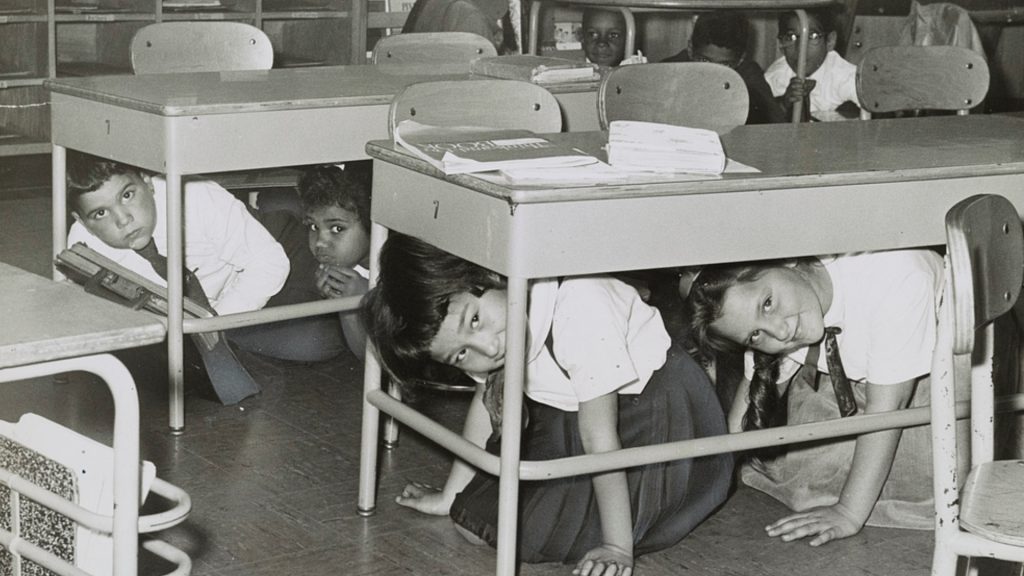

This fear of retaliation was known as Mutually Assured Destruction, or MAD for short. Most of us would agree that it was a form of madness to stockpile the most dangerous weapons known to man in the hope that nobody would ever use them.
Which Country Has The Most Nuclear Weapons?
A recent report broke down which countries have the most nuclear weapons. Russia came out on top with 6,000 known nuclear warheads. That’s a concern because Russia’s leader, Vladimir Putin, has taken an aggressive stance towards other countries, most notably Ukraine.

There are some in the US who believe that Putin is planning to launch a nuclear warhead into space. We have no way of knowing what would occur as a result. We also know that at least some of the nuclear weapons in the former Soviet Union are unguarded and vulnerable, which adds to the threat level.
How Many Nuclear Weapons Does The US Have?
Not far behind Russia is the United States, with an estimated 5,000 nuclear warheads. There’s no denying that’s a big number, but nuclear disarmament treaties have greatly reduced the United States’ total from where it was at its peak.

In 1967, under President Lyndon B. Johnson, the United States had an exponentially larger arsenal. How many nukes did we have? The total might surprise you: 32,000. That’s more than six times as many as we have now. As of 2024, 2,000 US nuclear warheads are fully deployed and ready to be used.
China Is Still Building An Arsenal
While many of the world’s largest nations have slowed their production of nuclear weapons, that’s not the case with China. The present estimate is that China has 500 nuclear warheads, putting them at number three. You might be surprised that they’re so far behind.

What’s more worrisome than China’s existing warhead count is the fact that they’re busy building additional warheads. Estimates from the Pentagon say that China could double their arsenal as soon as 2030. That’s only 6 years away and it doesn’t bode well for world peace.
Mortal Enemies With Nukes
There are some countries that always seem to be at war with one another. India and Pakistan both have nuclear weapons. Current estimates are that India has 165 warheads and Pakistan is slightly ahead with 170. Those nukes are a destabilizing influence in Asia.

Though the two countries are evenly matched in the arms race, the volatility of their situation is undeniably a risk. A launch by either country would impact that entire area of the world and could lead to an all-out nuclear war in a worst-case scenario.
Rogue Actors With Warheads
There are two countries where the risk of nuclear attacks seem particularly high. The first is North Korea. Its leader, Kim Jong Un, has conducted 220 missile tests since taking over from his father, Kim Jong Il. He has bragged about the country’s nukes.

The other country to be concerned about is Iran. While the international community has tried sanctions and inspections to prevent nuclear proliferation there, Iran is known to have an arsenal. What we don’t know is how big it is now or how big it could get.
What About Israel?
Israel has had a nuclear program since the 1960s. What makes Israel unusual is that the country has never admitted to having nuclear weapons. That makes it difficult to estimate the size of their arsenal, but estimates put the total around 90.

It’s widely believed that Israel has the ability to launch nuclear bombs by air. The country is in possession of the Jericho line of ballistic missiles. These have intercontinental range, which would mean they could launch against most of their neighbors in the Middle East.
Who’s Left And What’s Ahead
There are two countries we haven’t already mentioned: the United Kingdom and France. They have 225 and 300 warheads respectively. Most of the UK’s weapons are based on submarines at HM Naval Base Clyde in Scotland. France’s weapons are fully deployed and ready to be used, although they’ve cut their arsenal in half since the Cold War ended.

Any country that has nukes knows that launching one wouldn’t end well. The biggest risk comes from rogue nations such as North Korea and Iran and from unguarded nukes in Eastern Europe. If one of those fell into the wrong hands, we could be watching that second hand tick toward midnight.






